
Infertility, often regarded as a silent struggle, affects millions of individuals and couples worldwide. The inability to conceive a child naturally can be emotionally, physically, and financially draining. While advancements in medical science have offered hope through assisted reproductive technologies, understanding the underlying causes of infertility remains crucial for effective treatment and support. In this article, we delve into the multifaceted nature of infertility and explore its various causes.
Male Factor Infertility: Contrary to popular belief, infertility is not solely a female issue. Male factor infertility contributes to approximately 40-50% of all infertility cases. Causes may include:
Sperm abnormalities: Low sperm count, poor sperm motility, and abnormal sperm morphology can hinder fertilization.
Genetic factors: Conditions such as Klinefelter syndrome or chromosomal abnormalities can affect sperm production.
Lifestyle factors: Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, drug use, obesity, and exposure to environmental toxins can impair sperm quality.
Female Factor Infertility: Female infertility encompasses a wide range of conditions that affect reproductive health. Common causes include:
Ovulation disorders: Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or hormonal imbalances can disrupt ovulation.
Fallopian tube blockage: Blockages or damage to the fallopian tubes can prevent the egg from meeting the sperm.
Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, leading to inflammation and scarring.
Age-related decline: Advanced maternal age can lead to diminished ovarian reserve and decreased egg quality.
Uterine abnormalities: Structural issues within the uterus, such as fibroids or polyps, can interfere with implantation.
Unexplained Infertility: In some cases, despite thorough evaluation, the cause of infertility remains unknown. This can be frustrating for individuals and couples seeking answers and treatment options. Factors that may contribute to unexplained infertility include subtle hormonal imbalances, immune system dysfunction, or undetected genetic abnormalities.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors: Lifestyle choices and environmental factors play a significant role in fertility. Factors that can impact fertility include:
Smoking: Tobacco use can impair fertility in both men and women and increase the risk of miscarriage.
Excessive alcohol consumption: Heavy drinking can disrupt hormone levels and impair reproductive function.
Obesity: Obesity is associated with hormonal imbalances and can negatively affect ovulation and sperm production.
Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt hormone levels and interfere with reproductive processes.
Environmental toxins: Exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, and other environmental pollutants can affect fertility.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): Infections such as chlamydia and gonorrhea can cause inflammation and scarring of the reproductive organs. Autoimmune disorders: Conditions such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can affect fertility.
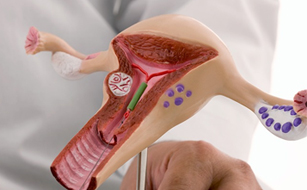
AIUI stands for Intrauterine Insemination. It's a fertility treatment that involves placing sperm inside a woman's uterus to facilitate fertilization.
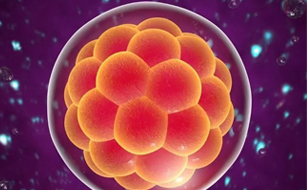
Blastocyst transfer represents a significant advancement in the field of assisted reproductive technology, offering hope to individuals and couples struggling with infertility. By extending embryo culture to the blastocyst stage, this technique allows for improved embryo selection
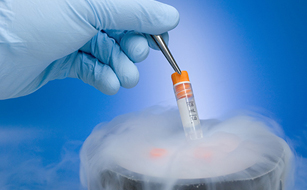
Embryo freezing has transformed the landscape of fertility treatment, offering individuals and couples facing infertility a valuable option for preserving and expanding their reproductive options. By cryopreserving embryos, individuals can increase their chances of pregnancy, reduce the risk of complications

High-risk pregnancy presents unique challenges and requires specialized care to ensure the health and well-being of both mother and baby. By understanding common risk factors, recognizing potential complications, and implementing appropriate management strategies, healthcare providers can help navigate the complexities of high-risk pregnancy and optimize outcomes for expectant

